Our Services
Co-creating sustainable business growth and development solutions
Business Strategy
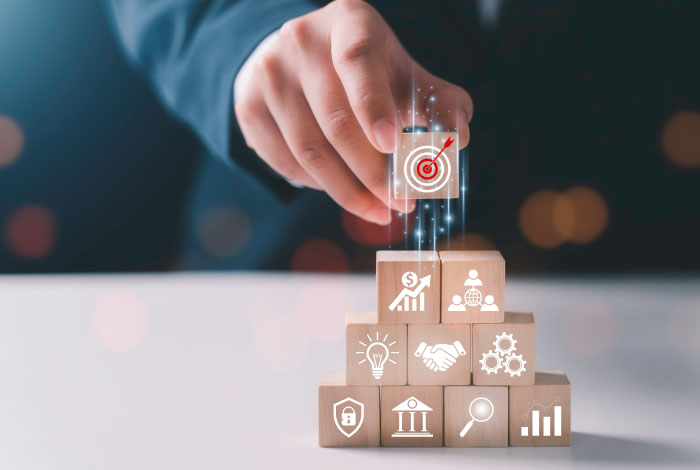

Act early to lower costs and protect the balance sheet so that you are stronger and leaner when the economy begins to turn more favourably.”
Companies that outperformed peers during the 2008 crisis cut operating costs by 1 percent before the downturn.
The goal of strategy is to maximize long-term value by:
1. A better understanding of your business environment to identify strategic opportunities for new and existing clients, products and services.
2. The ability to establish, maintain and nurture existing and new business relationships, through effective communication skills for long-term value creation.
3. A business development plan and the ability to critically assess and pursue new business opportunities.
Technology
Throughout history, technology has consistently changed the way workers across every industry do their jobs. From the industrial age to modern day, technology has improved working conditions. Its impact on the work environment has streamlined tedious and environmentally wasteful processes, expedited access to work while exponentially increasing productivity and made working from anywhere easier than ever.
Workers today are more productive than they’ve ever been. The impact of technology on work, both in manufacturing and in communication, has exponentially increased the rate of production and speed at which business occurs.
Technology in the workplace has helped workers become more efficient than ever before. What used to take hours now can take minutes. Messages can be sent instantly to colleagues or clients across the world. Payments or proposals can be transferred almost immediately.
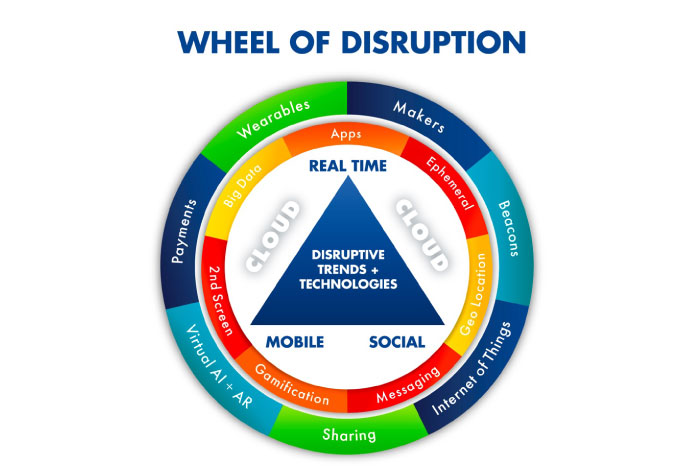
Twelve emerging technologies—including the mobile Internet, autonomous vehicles, and advanced genomics—have the potential to truly reshape the world in which we live and work.
Leaders in both government and business must not only know what’s on the horizon but also start preparing for its impact.
Almost every advance is billed as a breakthrough, and the list of “next big things” grows ever longer. Not every emerging technology will alter the business or social landscape—but some truly do have the potential to disrupt the status quo, alter the way people live and work, and rearrange value pools.
It is therefore critical that business and policy leaders understand which technologies will matter to them and prepare accordingly.

Customer Disruptions
The pandemic disrupted customer loyalty strategies.
When it comes to interactions between customers and brands, it could be said that COVID-19 changed nearly everything. Traditional strategies and tactics that brands have used to engage with consumers, deliver an exceptional experience, and earn loyalty and repeat purchases have been upended by a pandemic of historic proportions. The disruptions have touched almost every aspect of our daily lives as consumers. The disruption of the past 18 months has created new consumer behaviours (and, in some cases, new consumer profiles), many of which we expect to continue even after we fully emerge from the pandemic. Brands must recognize that many of the “orthodoxies” that existed prior to the pandemic have been changed forever, requiring re-examination of the traditional approaches to building customer loyalty.
TAX SERVICES
The South African Revenue Service (SARS) has introduced an enhanced Tax Compliance Status System.
Being tax compliant and ‘paying your fair share’ is not just good for you, but also contributes to the positive growth of our country’s economy which in turn benefits all South Africans.
South African Revenue Service (SARS) Commissioner Edward Kieswetter has warned non-compliant taxpayers and traders that the revenue authority will not tolerate any transgressions of tax and customs laws. The revenue service is ready to act firmly and professionally with those that engages in these practices.
SARS’ primary objective is to provide clarity and certainty for taxpayers and traders wishing to comply with their legal obligation by making its easy and seamless to do so. The organization is also enhancing its capability to detect and make it costly for those who are determined to be non-compliant.
In this regard, Commissioner Kieswetter said that compliance with these laws was essential so that SARS could discharge its responsibility to collect enough revenue to ensure that South Africa is able to invest in the growth and development of the country and improve the well-being of all.
“Tax crime is not a victimless crime. It directly affects the poorest of the poor who are dependent on basic services including the social security safety net for old age pensioners, child grants and for tertiary education support targeting needy students as well as providing health services, among others.
“SARS is therefore determined to enforce the tax and customs laws of the country without fear or favour in a responsible manner when all other legal avenues have been exhausted”.

Health and Safety

Employee health and safety programs should be a major priority for management because they save lives, increase productivity, and reduce costs. These health and safety programs should stress employee involvement, continued monitoring, and an overall wellness component (Anthony et al., 2007). Work safety requires that safe working conditions should not create significant risk of people being rendered unfit to perform their work. Health and safety at work is therefore aimed at creating conditions, capabilities, and habits that enable the worker and his/her organization to carry out their work efficiently and in a way that avoids events which could cause them harm (Garcia-Herrero et al., 2012). It is clear that safe working conditions have an effect on the habits of workers, which in turn impacts on efficiency. This implies that employees working in a safe condition are likely to perform in a way that will not cause them harm.
Risk Management
There is a growing spotlight on sustainability and environmental, social and governance (ESG) issues. The Global Risk Report 2022 from the World Economic Forum listed the consequences of climate inaction, nature loss, and erosion of societal cohesion as the most severe risks on a global scale over the next 10 years.
To tackle these risks, the report calls for a “whole-of-society” response, engaging different sectors to lead individual actions towards an end goal that benefits long-term well-being and prosperity.
Now, more than ever, is it critical to embed ESG, and specifically nature, into business practices and act on findings like those in the WEF’s Global Risk Report.

Legal

Taking steps to meet your legal obligations might seem like a management no-brainer, but only fulfilling your minimum requirements might result in missed opportunities. Understanding the reasons for the various rules, laws and regulations that govern your business will help you take advantage of any benefits they offer while ensuring you stay in compliance at all times.
In its business sense, “compliance” refers to a company meeting its legal obligations.
Simple examples of compliance includes obtaining a business license, correct registration with the requisite authorities and paying your taxes. The importance of compliance is more evident as issues become more complex when your business grows. The way you make and sell your product and service might fall under the auspices of a government agency, such as a restaurant needing to meet health department guidelines.
The most obvious consequence of compliance is that it decreases your risk of fines, penalties, work stoppages, lawsuits or a shutdown of your business.
Labour Relations
Many business compliance issues deal with protecting employees. The more employees feel they work in a fair, professional and safe environment, the more likely they will be committed to stay with you. Even if you don’t harass or discriminate against any employees, if you don’t take steps to ensure none of your employees do, you can lose valuable workers. Include policies and procedures in your employee handbook that mirror your legal compliance obligations. Remember, a policy is only strong if it is enforced. Your policy should not only present the rules but also specify the procedure for dealing with infractions, such as a reprimand and additional training on a first infraction and suspension or termination for a second.
You will have expanded responsibilities regarding your workers, covering hiring, firing, discrimination, harassment, safety, wages, payroll and benefits.

Business Rescue
As a result of financial difficulties experienced during the South African lockdown period, many companies are at the crossroads of having to choose between liquidation and business rescue. Some are still able to function but are likely to become factually and commercially insolvent within the next six months. Deciding whether or not to apply for business rescue can be a difficult task. To help you make an informed decision, we look at the advantages of corporate business rescue and consider a few important factors below.
An important factor to consider is whether the company is in financial distress or whether it is just an attempt to stay legal proceedings against it. As such, before a company can enter business rescue, it is important to determine whether it meets the requirements of financial distress.

The main purpose of the rescue proceedings is to rehabilitate a company that is in financial distress. Such a company is unable to pay debts due or is likely to become unable to pay debts within six months from the date of the investigation. Its liabilities exceed its assets or are likely to do so within the next six months.
Only in the instance where a company can be rehabilitated is corporate business rescue recommended. The process entails a thorough analysis of the company’s financial state, its affairs, debts, assets, and operations. The company is brought under temporary supervision of a qualified and experienced business rescue practitioner who oversees the process of bringing the company back to a state in which it can trade and fulfil its obligations.
Market Research

Global trends indicate that the small medium and micro enterprises (SMMEs) sector has experienced sustained growth and is consistently the largest employer in both the developed and developing world in recent times.
Research shows that in the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) area, SMMEs represent almost the totality of the business population, accounting for about 70% of employment and generate between 50% and 60% of the value added to the economy.
In Africa, this sector forms the backbone of most countries’ economies, representing more than 90% of businesses and employing more than 60% of workers, many of whom are women and youth.
The situation in South Africa is markedly different as SMMEs are experiencing stagnation in the turnover generated and in employment growth.
A 2017 study by Small Business Institute (SBI) found that 70% of emerging small businesses failed within the first two years of operation. The same study revealed that while 98.5% of the country’s economy is made up of SMMEs, they only delivered 28% of all employment opportunities.
Worryingly, 56% of jobs in South Africa are created by the 1 000 largest companies and government. This contrasts sharply with the contribution of SMMEs in OECD countries and elsewhere on the continent.
The SBI report warned that the National Development Plan’s (NDP’s) goal of small businesses creating 90% of jobs by 2030 would not be realised unless this vital segment of the economy received the necessary support.
The success of SMMEs in South Africa is critical, given the high levels of unemployment and poverty. It is generally accepted that SMMEs create more job opportunities across geographic areas and sectors, and employ broad segments of the labour force. This includes the absorption of low skilled workers – a hallmark of the country’s economy.
Nurturing these small enterprises could also help broaden South Africa’s skills base as SMMEs provide opportunities for skills development better than large firms.
A key feature of small businesses is that they contribute to inclusion by serving locations, populations and markets that do not have enough scale to attract larger firms, thus creating new demands and markets.
One of the hurdles to the success of SMMEs is the lack of access to markets for products and services. With the rise of globalisation, market access is rapidly and constantly changing due to sustainability and product standards, industry regulations, certification, customs procedures and requirements in foreign markets.
Adopting these is costly for SMMEs because their implementation is sometimes arduous and cumbersome, which negatively affects buddying enterprises.
Globally, value and local chains are dominated by large companies, and these usually determine the requirements and standards that need to be adopted and used for producing products and services. The domination by large companies of different value chains make it difficult for small business to operate outside of the value chain. Therefore, working within these value chains offers SMMEs market access opportunities to participate in global and local markets.
The SMMEs can be integrated into the global and value chains in different ways. For example, as exporters or/and suppliers to large firms that export. Stronger participation by SMMEs in global markets creates opportunities to scale up and enhance productivity, accelerate innovation, facilitate technology spill overs and managerial know-how, broaden and deepen the skill-set.
International exposure – be it through imports, exports or foreign direct investment – frequently goes hand in hand with higher productivity and wages.
Business Services
-
Accounting
-
Taxation
-
Advisory
-
HR
-
Business Funding
-
Data Services
-
Marketing
-
Company Registrations (CIPC)
-
Company Annual Returns (CIPC)
Beneficial Ownership

ABOUT BENEFICIAL OWNERSHIP (Extract from CIPC)
The Companies and Intellectual Property Commission (CIPC) launched its beneficial ownership (BO) register for companies and close corporations on 1 April 2023.
The aim of establishing the BO register is to have a repository/register of natural persons who own or exercise control over legal entities; to assist law enforcement with relevant information when it comes to their investigations of who the ultimate owners of an entity are; and to mitigate the risks identified in the national risk assessment where legal persons were identified as vehicles prone to abuse for money laundering and terror financing activities. The register to be kept is for the applicable companies and close corporations to submit any beneficial ownership information relating to that entity. Anyone with more than 5% beneficial ownership of a company or close corporation must submit (file) with the CIPC, the requisite information.
Any individual whose direct or indirect beneficial ownership of the company is 5% or greater.
The following needs to be completed for every beneficial owner:
- Full names and surname
- Date of birth
- Identity or passport number
- Residential address
- Postal address
- Email address
- The extent of the individual’s ownership or effective control over the company.
No. The only people allowed to access it will be law enforcement and competent authorities.
The most likely consequence is a compliance notice, followed by an administrative fine. Other consequences include the triggering of other investigations and in serious cases, the disqualification of directors.
– The holding of beneficial interest in the securities of a company;
– Control over voting rights, or control over the exercise of voting rights associated with securities of a company;
– The exercise of the right to appoint / remove members of the board of directors of a company,
OR control over the exercise of the right to appoint / remove board members;
– The holding of beneficial interests in the securities of a holding company, (through a subsidiary)
OR the ability to exercise control (including through a chain of ownership) of a holding company through its subsidiary;
– The ability to exercise control, through a chain of ownership, of-
(i) A juristic person other than a holding company of that company;
(ii) A body of persons corporate or unincorporate (i.e body corporate of an estate – NPC);
(iii) A person acting on behalf of a partnership;
(iv) A person acting in pursuance of a trust or agreement (i.e trustees, beneficiaries of trusts, beneficiaries of an agreement);

Funding

SHORT TERM FUNDING
Get up to R5M in fast & easy business funding.. |
Flexible Funding Solutions for your Business* |
- REVOLVING FACILITY,
- BRIDIGING FACILITY,
- SHORT TERM WORKING CAPITAL
Your repayments will be over 3, 6, 9 or 12 months - or repay early and save.
LONG TERM FUNDING
- WORKING CAPITAL
- TRADE FINANCE
- EQUIPMENT FINANCE
- EXPANSION FUNDING
WE PREPARE YOUR LOAN APPLICATIONS FOR BANKS AND DEVELOPMENT FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS. *(Terms and conditions apply)
NEED ASSISTANCE WITH SOUTH AFRICAN REVENUE SERVICES (SARS)
DEBT MANAGEMENT
- Owing SARS money is stressful enough
- We assist:
- Negotiation with SARS
- Settlement Negotiation
- Compromise
- Deferral
- Tax Audits
- Appeals
- Objection
- Alternate Dispute Resolution (ADR)
- Voluntary Disclosure (VDP)

ADDITIONAL SERVICES
- Online Computer Systems and Software (incl. Cloud Services)
- Annual Financial Statements
- Management Statements
- VAT201 Submissions
- EMP201 Submissions
- EMP501 employer reconciliations
- All CIPC services
- BBB-EE Certificates
- Independent Reviews
- Accounting Officer Reports
- Statutory Returns (Unemployment Insurance Fund)
- Income Tax Returns (For all entities)
- Provisional Tax Returns (For all entities)
- Income Tax Registrations (For all entities)
- VAT Registrations (For all entities)
- Payroll Registrations (PAYE/UIF & SDL)
- Company Registrations
